

Section Guide
Imagine waking up one morning to find more hair on your pillow than usual. The fear of hair loss, or alopecia, can be unsettling, especially for women who often face unique challenges related to this condition. Female alopecia isn’t just about losing hair—it’s about the emotional and psychological impact it can have. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take control and make informed decisions.
Causes of Female Alopecia
1. Hormonal Imbalances
- Hormonal imbalances are one of the most significant contributors to female alopecia.
- Women experiencing conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders often face hair thinning due to disrupted hormone levels.
- Estrogen and progesterone, which play crucial roles in hair growth, can become unbalanced due to various factors, leading to hair loss.
- For instance, after childbirth or menopause, women may experience a significant shift in hormones, which can trigger hair loss.
- What You Can Do: If you suspect hormonal imbalances, consult a healthcare provider.
- They might recommend hormone tests to identify any issues.
- Managing conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders through medication or lifestyle changes can help alleviate hair loss symptoms.
2. Genetics
- Genetics play a pivotal role in female-pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. This hereditary condition leads to gradual thinning of the hair, often starting at the part line or crown.
- If your family has a history of hair loss, you might be genetically predisposed to experience it as well. This type of hair loss is usually progressive, meaning it can worsen over time if not managed effectively.
- What You Can Do: While you can’t change your genetics, you can take proactive steps to manage hair loss.
- Early intervention with treatments like minoxidil or consulting a dermatologist can help slow down the progression and improve hair density.
3. Stress
- Stress, both emotional and physical, can trigger a type of hair loss known as telogen effluvium. This condition occurs when stress pushes hair follicles into a resting phase, leading to increased shedding.
- Major life events, such as the death of a loved one or a significant life change, can lead to noticeable hair loss. However, stress-induced hair loss is often temporary, and hair can return to its normal growth cycle once stress levels decrease.
- What You Can Do: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine.
- Practices such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels. Additionally, seeking counseling or therapy can provide support and coping strategies.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies
- A well-balanced diet is crucial for maintaining healthy hair. Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, vitamin D, and biotin can lead to hair thinning and loss.
- For example, iron deficiency anemia can significantly impact hair growth, as iron is vital for producing hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to hair follicles.
- What You Can Do: Evaluate your diet and consider incorporating foods rich in hair-friendly nutrients.
- Spinach, eggs, nuts, and fish are excellent sources of iron and biotin. You might also consider taking supplements if you have specific deficiencies, but consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.


5. Medical Treatments
- Certain medical treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, can lead to temporary hair loss.
- While these treatments are essential for combating serious illnesses like cancer, they can significantly affect hair growth. The good news is that hair often regrows after the completion of treatment, though it may initially grow back in a different texture or color.
- What You Can Do: If you’re undergoing treatment that may cause hair loss, talk to your healthcare team about potential hair preservation options.
- Some treatments, such as cold caps, can help minimize hair loss during chemotherapy. Additionally, consider using gentle hair care products to reduce further damage.


6. Autoimmune Diseases
- Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden, patchy hair loss.
- This condition can be particularly distressing as it may cause hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or other areas of the body.
- Although alopecia areata can affect anyone, it often begins in childhood or early adulthood.
- What You Can Do: Treatment options for autoimmune-related hair loss may include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation or immunotherapy to stimulate hair regrowth.
- Consulting with a dermatologist who specializes in autoimmune conditions can provide a tailored treatment plan.
7. Poor Hair Care Practices
- Your daily hair care routine can significantly impact the health of your hair.
- Excessive use of heat styling tools, harsh chemicals, and tight hairstyles can weaken hair and lead to breakage and thinning.
- Practices like frequent coloring, perming, or tight ponytails can contribute to traction alopecia, where hair loss occurs due to pulling on the hair.
- What You Can Do: Opt for a more gentle hair care routine.
- Use sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners, and limit the use of heat styling tools.
- Choose hairstyles that don’t pull tightly on the hair, and avoid harsh chemical treatments. Regularly trimming your hair can also help prevent split ends and breakage.
Symptoms of Female Alopecia
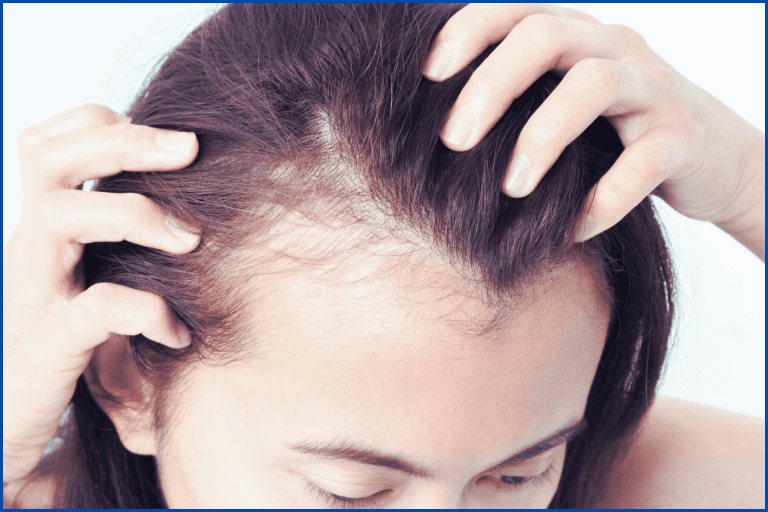


- Thinning Hair: A gradual thinning of hair, especially around the part line or crown, is one of the earliest signs. This may start with the hair becoming less dense and more fragile.
- Bald Spots: In conditions like alopecia areata, small, round patches of hair loss may appear. These patches can vary in size and may occur suddenly.
- Excessive Shedding: Finding more hair than usual on your pillow or in your brush can be a sign of excessive shedding. This can be alarming but often resolves once the underlying cause is addressed.
- Receding Hairline: Female-pattern baldness may cause the hairline to recede, particularly around the temples. This can lead to a more noticeable thinning of hair at the hairline.
Treatment Options for Female Alopecia
1. Medications
Medications can play a crucial role in managing hair loss. Minoxidil, an over-the-counter topical treatment, is FDA-approved for stimulating hair growth. It works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting new hair growth. Finasteride, a prescription medication, can help by blocking the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) that contributes to hair loss. However, finasteride is more commonly used in men.
What You Can Do: Consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable medication for your condition. They can guide you through the benefits, potential side effects, and how to use these treatments effectively.
2. Hormone Therapy
For hair loss related to hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy can be beneficial. This might include treatments to address thyroid issues or hormonal contraceptives to regulate hormone levels. Hormone therapy aims to restore hormonal balance, which can help mitigate hair loss.
What You Can Do: Discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider who can evaluate your hormonal levels and recommend appropriate hormone therapy if needed. Monitoring hormone levels regularly can help manage hair loss more effectively.
3. Nutritional Supplements
Nutritional supplements can help address deficiencies that contribute to hair loss. Supplements like biotin, iron, and vitamin D are often recommended to support hair health. These nutrients are essential for maintaining healthy hair follicles and promoting growth.
What You Can Do: Consider taking supplements if you have identified specific deficiencies. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure they are appropriate for your needs.
4. Hair Transplant Surgery
For more severe cases of hair loss, hair transplant surgery might be a viable option. This procedure involves relocating hair follicles from one part of the scalp to thinning areas. The transplanted hair follicles continue to grow naturally, providing a permanent solution to hair loss.
What You Can Do: If you’re considering hair transplant surgery, research reputable clinics and consult with experienced surgeons. They can evaluate your suitability for the procedure and discuss the expected outcomes and recovery process.
5. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly impact hair health. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques, a balanced diet, and gentle hair care practices can all contribute to healthier hair. Ensuring adequate hydration and regular exercise can also support overall well-being and hair growth.
What You Can Do: Implement lifestyle changes gradually and monitor their impact on your hair health. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients and practicing stress management techniques can help support hair growth and overall health.
6. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as hair thickening fibers and sprays, can temporarily enhance the appearance of thinning hair. These products work by adding volume and coverage to the hair, helping to boost confidence while exploring other treatment options.
What You Can Do: Explore different topical treatments to find those that best suit your needs. These products can provide a cosmetic solution while you address underlying causes of hair loss with more permanent treatments.
7. Counseling and Support Groups
The emotional impact of hair loss can be profound. Seeking support from counseling or joining support groups can provide comfort and practical advice. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can offer emotional support and coping strategies.
What You Can Do: Reach out to support groups or counseling services that specialize in hair loss. These resources can help you navigate the emotional aspects of alopecia and connect you with others who understand your journey.
Practical Steps for Managing Female Alopecia
- Regular Scalp Care: Maintaining a clean and healthy scalp is essential for hair health. Use mild shampoos and conditioners that are free of harsh chemicals. Regular scalp massages can also stimulate blood flow and support hair growth.
- Avoid Heat and Chemicals: Minimize the use of heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments. Opt for natural, nourishing hair care products that promote healthy hair without causing damage.
- Monitor Your Diet: Ensure your diet includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Incorporate sources of iron, biotin, and vitamin D to support hair growth. Regularly evaluate your diet and make adjustments as needed to address any deficiencies.
Conclusion
Female alopecia can be a challenging and emotional journey, but understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring a range of treatment options can empower you to take control of your hair health. Whether your hair loss is due to hormonal imbalances, genetics, stress, nutritional deficiencies, or other factors, there are numerous strategies and treatments available to help manage and potentially reverse hair loss.
Taking proactive steps for alopecia, such as consulting with healthcare professionals, adopting a balanced diet, and incorporating gentle hair care practices, can significantly impact your hair’s health and appearance. Remember, hair loss is not just a physical issue—it affects self-esteem and confidence, making emotional support and counseling valuable components of your overall strategy.
Empower yourself with knowledge and resources about alopecia, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed. By addressing the root causes and exploring effective treatments, you can navigate the challenges of female alopecia with confidence and optimism.
For ongoing support and the latest information on managing hair loss, refer to reputable resources like the American Academy of Dermatology, the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, and Mayo Clinic. Taking these steps will not only aid in managing your hair loss but also support your overall well-being and self-esteem.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right approach, you can achieve healthier hair and a renewed sense of confidence.
Additional Resources for More Information
For further information on managing female alopecia and exploring treatment options, consider visiting these reputable resources:
- American Academy of Dermatology: Hair Loss
- National Alopecia Areata Foundation
- Mayo Clinic: Female Pattern Baldness
Understanding and managing female alopecia requires a combination of medical insight, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the challenges of hair loss and take steps toward restoring confidence and hair health.