Chest pain is a symptom that can strike fear into anyone. It’s often associated with heart disease, but the reality is that chest pain can stem from a variety of sources—some serious, others less so. Understanding the diverse causes of heart pain is essential for effective management and timely treatment. Whether it’s a sudden, sharp ache or a persistent, dull discomfort, pinpointing the root cause of heart pain can make a significant difference in how you address it.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven surprising causes of heart pain, providing you with the information you need to recognize symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and take preventive measures. Let’s dive into the multifaceted world of chest pain.
Table of Contents

1. Cardiac Causes: More Than Just a Heart Attack
When people think of chest pain, they often immediately think of heart problems. Indeed, cardiac causes are among the most serious and warrant immediate medical attention. Here are some key cardiac conditions that can cause chest pain:
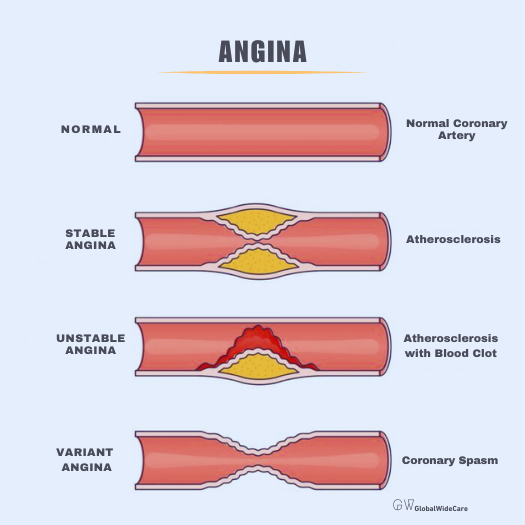
- Angina: This condition occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Angina often presents as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the chest. It may also radiate to the shoulders, neck, or arms. Angina usually occurs during physical activity or emotional stress and is relieved by rest or medication.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A heart attack happens when one or more coronary arteries become blocked, preventing blood flow to the heart muscle. Symptoms of a heart attack include severe heart pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness. This condition requires immediate medical intervention to minimize damage to the heart.
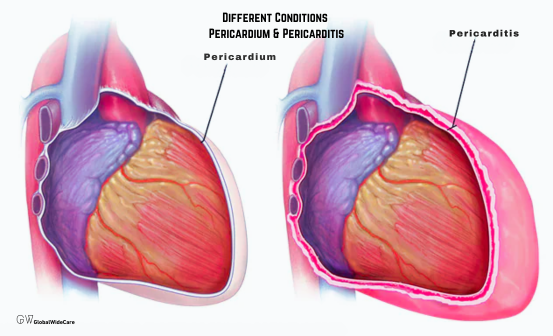
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, the protective sac surrounding the heart, can lead to sharp, stabbing heart pain. The pain may worsen with deep breathing or lying down and improve when sitting up or leaning forward. Treatment often involves anti-inflammatory medications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Cardiac Causes
- Pressure or squeezing in the chest
- Pain radiating to the arms, neck, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or sweating
If you experience these symptoms, seek emergency medical care immediately.


2. Gastrointestinal Issues: The Surprising Link
Not all chest pain is related to the heart. Gastrointestinal issues can also be a significant source of discomfort. Common gastrointestinal causes of heart pain include:
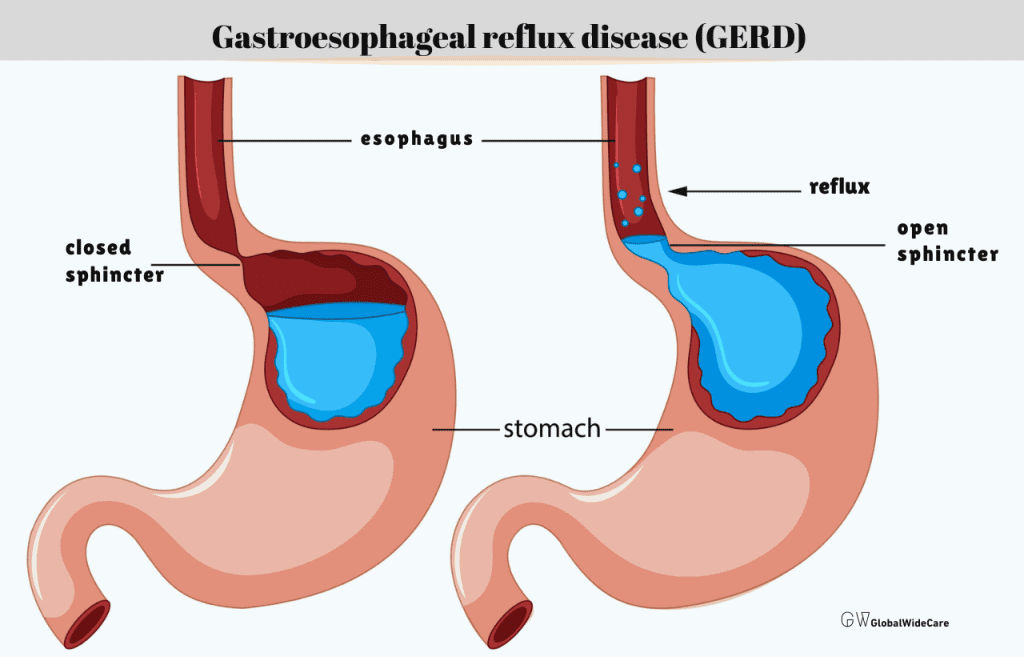
- Acid Reflux (GERD): Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. This can lead to a burning sensation in the chest known as heartburn. GERD symptoms often worsen after eating, when lying down, or during periods of stress.
- Esophageal Spasms: These are irregular contractions of the esophagus that can cause sudden, severe heart pain. The pain may mimic that of a heart attack and can be triggered by eating hot or cold foods, or even by stress.
- Peptic Ulcers: Sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine can cause pain in the chest area. The pain is often described as a dull ache or burning sensation and may be relieved by antacids or medications that reduce stomach acid.
Identifying Gastrointestinal Pain
- Burning or aching sensation in the chest
- Pain after eating or lying down
- Pain relieved by antacids or dietary changes

3. Musculoskeletal Problems: The Hidden Culprits
Chest pain resulting from musculoskeletal issues can often be mistaken for cardiac pain. Here’s what you need to know:
- Costochondritis: This is the inflammation of the cartilage where the ribs attach to the sternum. It can cause localized chest pain that worsens with movement or palpation. The pain is typically sharp and can be reproduced by pressing on the affected area.
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or trauma to the chest muscles can lead to pain that feels like a constant ache or sharp discomfort. Activities that involve heavy lifting or sudden movements can strain the muscles and lead to heart pain.
- Rib Injuries: Fractured or bruised ribs can cause significant pain, especially with movement or deep breathing. This type of pain is usually localized to the area of the injury and may be accompanied by tenderness.
Signs of Musculoskeletal Pain
- Localized pain that worsens with movement
- Tenderness upon palpation
- Pain with deep breathing or coughing
4. Pulmonary Conditions: Breathing Issues and Chest Pain
Pulmonary conditions can also cause chest pain, often accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing or coughing:
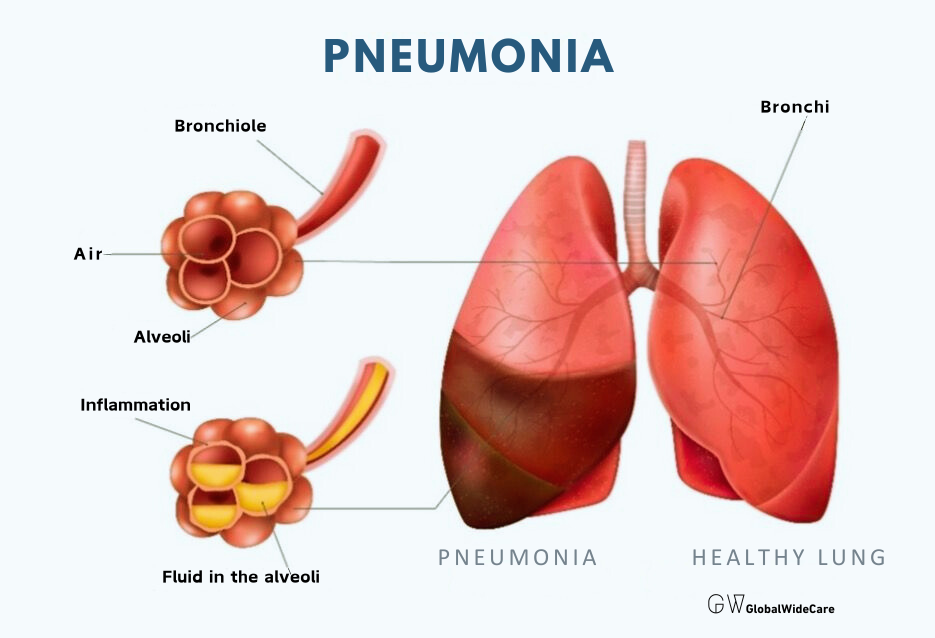
- Pneumonia: An infection of the lungs that causes inflammation and fluid buildup can lead to sharp, pleuritic chest pain. This pain is often worsened by deep breaths or coughing and may be accompanied by fever, chills, and a productive cough.
- Pleuritis: Inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the lungs, can cause sharp pain that worsens with breathing or coughing. Pleuritis is often a complication of other respiratory infections or conditions.
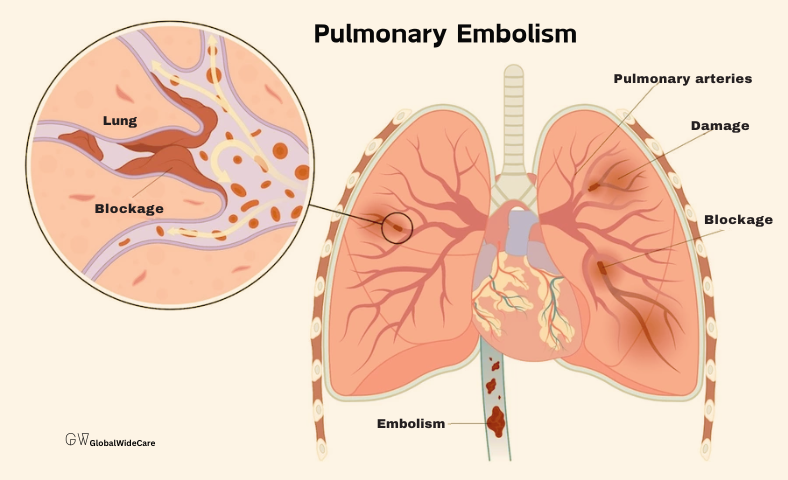
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries, usually caused by a blood clot, can result in sudden, sharp heart pain and shortness of breath. This condition is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Recognizing Pulmonary-Related Pain
- Sharp, pleuritic pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever or productive cough


5. Psychological Factors: Anxiety and Stress
Chest pain is not always due to physical conditions. Psychological factors can play a significant role:
- Panic Attacks: These can cause intense, sudden heart pain along with feelings of dread, palpitations, and dizziness. The pain is often sharp and can be accompanied by a sense of impending doom.
- General Anxiety: Chronic anxiety can lead to muscle tension and tightness in the chest, resulting in discomfort or pain. This type of pain may be associated with other anxiety symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat or sweating.
Identifying Psychological Causes
- Sharp or pressure-like pain with accompanying anxiety symptoms
- Pain associated with panic attacks or stress
- Relief with relaxation techniques or anxiety management
6. Other Causes: Less Common but Significant
Several less common conditions can also lead to chest pain:
- Shingles: An outbreak of shingles can cause pain along the chest if the rash affects the thoracic nerves. The pain is often described as burning or tingling and may precede the appearance of the rash.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications can cause chest pain as a side effect. This is usually described in the medication’s warning label, and it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider if you suspect your medication is causing discomfort.
7. When to Seek Medical Help
While many causes of chest pain are manageable with appropriate care, some require immediate attention. Here’s a quick guide on when to seek medical help:
- Sudden, severe chest pain: If you experience intense pain, especially if it’s accompanied by shortness of breath, nausea, or sweating, seek emergency care.
- Persistent or worsening pain: If heart pain doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medications or lifestyle changes, consult a healthcare professional.
- Pain with other symptoms: If heart pain is accompanied by symptoms like fainting, dizziness, or severe difficulty breathing, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion: Managing Chest Pain with Knowledge and Care
Chest pain is a complex symptom with a wide range of potential causes. Understanding these causes can help you make informed decisions about your health and seek appropriate treatment. From cardiac conditions to gastrointestinal issues, musculoskeletal problems, pulmonary conditions, and psychological factors, each cause requires a unique approach for management and treatment.
By staying informed, monitoring your symptoms, and seeking timely medical advice, you can navigate the challenges of chest pain more effectively. Remember, while it’s important to recognize common causes, only a healthcare professional can provide a definitive diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Take charge of your health with knowledge and proactive care, and you’ll be better equipped to manage chest pain effectively.
Additional Resources for More Information
For further details on the causes and management of heart pain, check out these informative resources:
By expanding your knowledge and taking proactive steps, you can effectively manage heart pain and ensure your health remains a priority.