Imagine this: You’re enjoying a meal with friends, laughter fills the air, and suddenly, a sharp pain twists in your abdomen. Abdominal pain can strike unexpectedly, disrupting your day and causing discomfort that ranges from mild to severe. But what’s really behind that pain, and more importantly, how can you effectively treat it? In this guide, we’ll explore the top seven causes of abdominal pain, offer solutions to alleviate it, and provide expert insights to help you manage your symptoms.
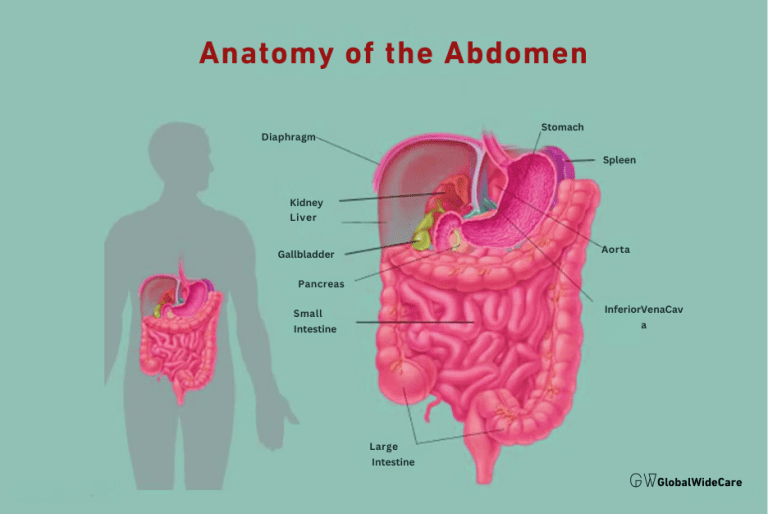
Table of Contents
The Mysterious World of Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a broad term that encompasses a variety of sensations, from dull aches to sharp, stabbing pains. It can be challenging to pinpoint the exact cause, as your abdomen houses many vital organs. The complexity of this area means that abdominal pain can stem from various issues, some minor and others more serious.
The Top 7 Causes of Abdominal Pain
Understanding the root of your pain is the first step toward effective treatment. Here are the seven most common causes:
- Digestive Issues: Problems like indigestion, constipation, and gas can cause significant discomfort. These issues often result from dietary choices, such as consuming too much fatty or spicy food. Indigestion, for example, occurs when your stomach has difficulty processing food, leading to a feeling of fullness, bloating, and sometimes pain. Constipation, on the other hand, is often caused by a lack of fiber or water in your diet, leading to hard stools that are difficult to pass. Gas pain is another common culprit, often triggered by swallowing air or eating foods that produce gas, such as beans and carbonated beverages.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis can cause chronic abdominal pain. These disorders are often accompanied by symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. IBS, for instance, is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine and can lead to alternating periods of constipation and diarrhea, along with cramping and abdominal pain. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract causes severe pain, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause inflammation in the stomach and intestines, leading to pain. Gastroenteritis, often referred to as the stomach flu, is a common culprit. This condition causes the lining of the stomach and intestines to become inflamed, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and cramping. Food poisoning is another example, often caused by consuming contaminated food or water, leading to similar symptoms.
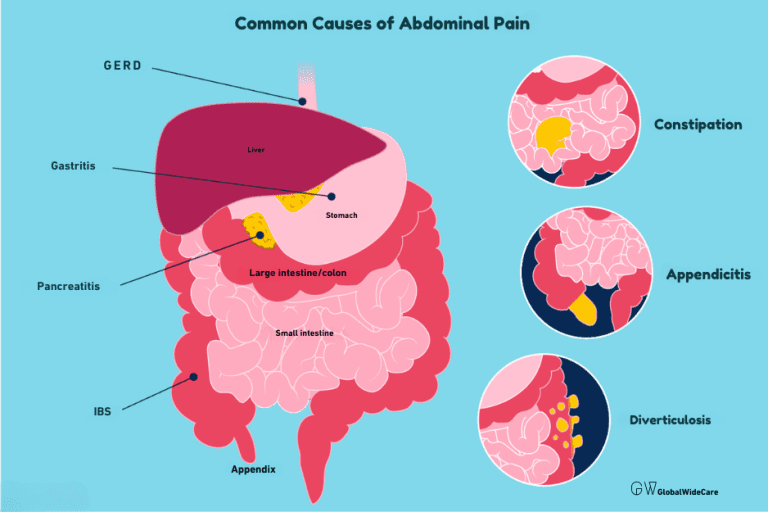

4. Gallstones: These hard deposits in the gallbladder can block the bile ducts, causing intense pain, particularly after eating fatty foods. Gallstones are typically formed when there’s an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, leading to the crystallization of cholesterol or bilirubin. The pain from gallstones is often sharp and sudden, located in the upper right abdomen, and may radiate to the back or right shoulder. This condition, known as biliary colic, can last from a few minutes to several hours.
5. Appendicitis: A sudden pain that begins around your navel and shifts to the lower right abdomen could be a sign of appendicitis. This condition requires immediate medical attention, as the appendix can become inflamed and eventually burst if left untreated. The pain typically intensifies over a few hours and may be accompanied by fever, nausea, and loss of appetite. If the appendix ruptures, it can lead to a life-threatening infection known as peritonitis.
6. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Pain in the lower abdomen, coupled with a burning sensation during urination, may suggest a UTI. UTIs are more common in women due to the shorter length of the urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. In addition to abdominal pain, other symptoms may include a frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and fatigue. If the infection spreads to the kidneys, it can cause more severe symptoms, including back pain, fever, and chills.
7. Kidney Stones: These are solid mineral deposits that form in the kidneys and cause severe pain as they move through the urinary tract. The pain, often described as one of the most intense types of pain, typically starts in the back or side and radiates to the lower abdomen and groin. Other symptoms include blood in the urine, nausea, vomiting, and frequent urination. The size of the stone and its location determine the severity of the symptoms and the type of treatment required.
Additional Causes of Abdominal Pain
While the above are the most common causes, several other factors can contribute to abdominal pain:
- Peptic Ulcers: These are sores that develop on the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus, often due to an infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The pain is typically a burning sensation that occurs between meals or at night and may be relieved by eating or taking antacids.
- Menstrual Cramps: For women, menstrual cramps are a common cause of lower abdominal pain. However, severe pain could indicate conditions like endometriosis, where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, or fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths in the uterus.
- Hernias: A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. Abdominal hernias often cause a visible bulge and may result in pain, especially when lifting heavy objects, coughing, or bending over.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can cause upper abdominal pain that may radiate to the back. This condition can be acute or chronic and is often associated with heavy alcohol use, gallstones, or certain medications.
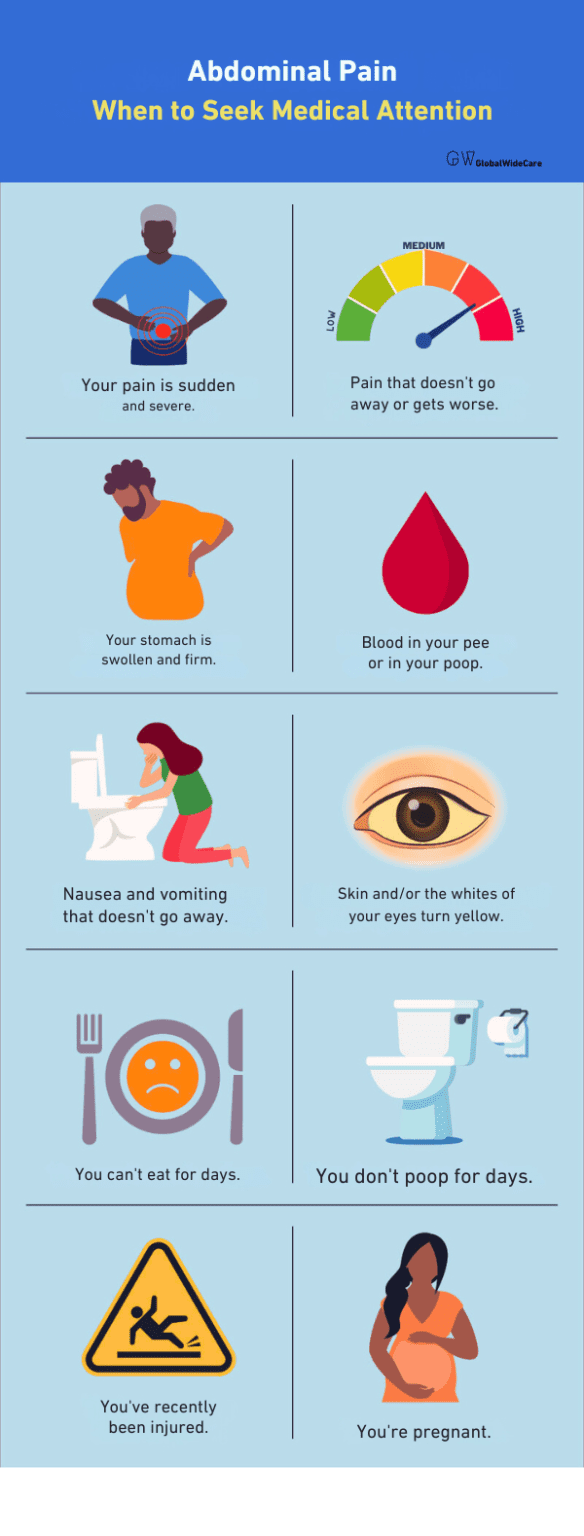
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some abdominal pain is harmless and resolves on its own, other symptoms warrant a trip to the doctor. Seek immediate medical help if you experience:
- Severe pain that comes on suddenly
- Pain accompanied by fever, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Blood in your stool or vomit
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent pain that lasts more than a few days
These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition that requires prompt medical intervention.
Effective Treatments for Abdominal Pain
Treating abdominal pain effectively depends on the underlying cause. Here are some general approaches:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Antacids, laxatives, and anti-gas medications can provide quick relief for minor digestive issues. However, these should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. For instance, antacids can neutralize stomach acid and provide relief from indigestion, while laxatives can help ease constipation.
- Home Remedies: Sometimes, simple home remedies can ease your discomfort. Drinking ginger tea, for example, can help reduce nausea and digestive discomfort due to its natural anti-inflammatory properties. Applying a warm compress to your abdomen or taking a warm bath can help relax muscles and reduce pain, especially in cases of menstrual cramps or muscle strain.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, and staying hydrated can prevent digestive-related abdominal pain. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet can also promote better digestion and prevent constipation.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate conditions like IBS, leading to more frequent abdominal pain. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels. Regular physical activity and adequate sleep are also crucial for maintaining overall well-being and reducing stress-related abdominal pain.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe or chronic conditions, your doctor may prescribe medications such as antibiotics for infections, antispasmodics for IBS, or proton pump inhibitors for ulcers. In cases of severe acid reflux or GERD, proton pump inhibitors can reduce stomach acid production and promote healing of the esophagus.
- Surgery: In cases of appendicitis, gallstones, or severe ulcers, surgery may be necessary to remove the source of the pain. For instance, a laparoscopic appendectomy is often performed to remove an inflamed appendix, while cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder to treat gallstones.

Long-Term Management and Prevention
Preventing abdominal pain involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here’s how you can reduce your risk:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit your intake of processed foods, caffeine, and alcohol. A balanced diet supports digestion and overall health, reducing the risk of developing conditions that cause abdominal pain.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes healthy digestion and can help prevent constipation, a common cause of abdominal pain. Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce the risk of gallstones and other related issues.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your digestive system running smoothly and prevents constipation. It also helps flush out toxins that can cause infections or other issues.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to what you eat and how you feel afterward. Avoid foods that trigger discomfort and eat smaller, more frequent meals to prevent overeating and indigestion. Chewing your food thoroughly and eating slowly can also aid digestion and reduce the likelihood of experiencing abdominal pain.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch potential issues early before they develop into more serious conditions. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the need for more invasive treatments.
Tips for Chronic Abdominal Pain
If you experience chronic abdominal pain, consider the following strategies:
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat and how your body reacts can help identify trigger foods and patterns that contribute to your pain. This information can be valuable for you and your healthcare provider in diagnosing and managing your condition.
- Consult a Specialist: If your pain persists despite treatment, it might be time to consult a gastroenterologist or another specialist. They can perform more specialized tests and provide targeted treatments.
- Consider Lifestyle Changes: Reducing stress, quitting smoking, and moderating alcohol consumption can significantly impact your digestive health and overall well-being. Implementing these lifestyle changes can reduce the frequency and severity of abdominal pain episodes.
External Resources for Further Information
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Abdominal Health
Abdominal pain can be a perplexing and often distressing experience, but understanding its causes and knowing how to address them can empower you to take control of your health. By identifying the root cause of your discomfort and applying the appropriate treatments, whether through simple dietary adjustments or seeking professional medical advice, you can effectively manage and even prevent future episodes of pain.
Remember, while some abdominal pain is temporary and harmless, persistent or severe pain should never be ignored. Early intervention can prevent more serious complications, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help you avoid many of the common causes of abdominal pain altogether.
Empower yourself with knowledge, listen to your body, and don’t hesitate to seek medical attention when necessary. With the right approach, you can minimize abdominal discomfort and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
Thank you for sharing this insightful article! I found the information really useful and thought-provoking. Your writing style is engaging, and it made the topic much easier to understand. Looking forward to reading more of your posts!